Interesting findings
Playing with the data, often strange patterns emerge. Some research led me to find the causes of these patterns, and here are a few of the interesting trends and correlation I found..
Click on the pictures below to zoom
Click on the pictures below to zoom
Energy consumption is often a good index of economic development
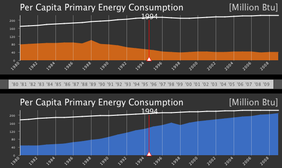
This may sound obvious, but it's interesting how the two things go well together! Take the example of North Korea and South Korea that is included in the application. On the top, you can see the North Korean economy that slowly goes down due to the big famine, the arduous march, on the 90's. I did some research, and this example is fitting because actually electricity became less and less available as the crisis continued.. road lights were the first to go off, especially outside the cities. In the end also factories didn't have any energy to produce more goods, creating a vicious circle that led to a complete collapse of the economy.
On the bottom you can see South Korea, where the opposite happened. In this case the big raise in energy consumption is due to the big economic development and is so steep thanks to how fast that country moved, also aided in this path by the U.S.A. and other western countries.
On the bottom you can see South Korea, where the opposite happened. In this case the big raise in energy consumption is due to the big economic development and is so steep thanks to how fast that country moved, also aided in this path by the U.S.A. and other western countries.
Wars in the Middle East.. and how the western countries survived
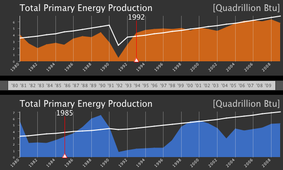
Kuwait on top, Iraq at the bottom. These two countries fought in 1991 (Iraq invaded Kuwait) and the repercussion of this war emerge clearly from these graphs..
First, population! When I saw such a drop I first thought that the war couldn't have cause half of the population to flee the country.. but actually it did! Kuwait was emptied in the span of a few months. It's energy production destroyed, since nobody was there anyway and the oil plants were methodically burnt bu the Iraqi Army.
Also Iraq is not so well off, as you can see on the bottom. Also, if you look at 2003 you see the dip in energy production caused by the last war. This time it's not so relevant.. after all the Americans didn't want to ruin the oil plants there.. on the contrary! Moreover, burning oil at random to obfuscate the skys was not useful anymore, thanks to GPS and laser tracked weapons.
First, population! When I saw such a drop I first thought that the war couldn't have cause half of the population to flee the country.. but actually it did! Kuwait was emptied in the span of a few months. It's energy production destroyed, since nobody was there anyway and the oil plants were methodically burnt bu the Iraqi Army.
Also Iraq is not so well off, as you can see on the bottom. Also, if you look at 2003 you see the dip in energy production caused by the last war. This time it's not so relevant.. after all the Americans didn't want to ruin the oil plants there.. on the contrary! Moreover, burning oil at random to obfuscate the skys was not useful anymore, thanks to GPS and laser tracked weapons.
Energy Consumption by Saudi Arabia
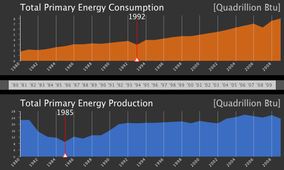
Saudi Arabia is an interesting case.. and it's not so easy to understand due to the international politics involved and the central role of this country in the global oil market.
First, we see a deep crisis in production in the 80's.. this is due to the 1980s oil glut crisis, which was a huge surplus of crude oil caused by falling demand following the 1970s Energy Crisis. The world price of oil went in 5 years from US$35 per barrel to below $10.
The really interesting thing is actually the energy consumption. In keeps increasing, steadily, always. Of course, energy is practically free there so the consumption is only limited by how much they need or care to use, but this article highlights potential problems caused by this positive trend on global oil price stability. In fact, such consumption rates could cause the price to rise (since less is available for exportation) and generate instability.
First, we see a deep crisis in production in the 80's.. this is due to the 1980s oil glut crisis, which was a huge surplus of crude oil caused by falling demand following the 1970s Energy Crisis. The world price of oil went in 5 years from US$35 per barrel to below $10.
The really interesting thing is actually the energy consumption. In keeps increasing, steadily, always. Of course, energy is practically free there so the consumption is only limited by how much they need or care to use, but this article highlights potential problems caused by this positive trend on global oil price stability. In fact, such consumption rates could cause the price to rise (since less is available for exportation) and generate instability.
Renewable Energies.. Europe Wins!
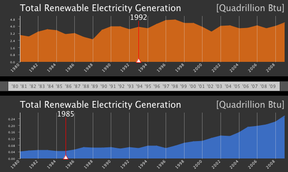
I know Europe is not just the U.K. but still.. This is impressive! Energy production is very relevant in the United States, as it is in Europe, but concerns for green energy did not yet take root in the new continent. The USA didn't even try to sign the Kyoto Protocol, and are the only big exception to this in the world. Also, in the application there's a History Page about the Kyoto protocol and it's influence to the carbon dioxide emissions you can have a look at.
Russia and its relevance..
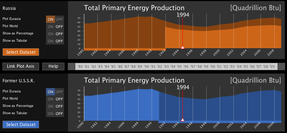
On top, Russia over Eurasia. On the bottom, the former USSR, always over Eurasia. First thing we notice is that Eurasia continues the plot of Former USSR perfectly. This is not a surprise, we know that Eurasia was, pretty much, the USSR!
What I found more interesting is that in the plot above, we see the trend of Russia and of Eurasia, and Russia in actually losing here in energy production.. The nation that was by far the most powerful and active in the area had, in fact, a very difficult time after the collapse of its communist system.
What I found more interesting is that in the plot above, we see the trend of Russia and of Eurasia, and Russia in actually losing here in energy production.. The nation that was by far the most powerful and active in the area had, in fact, a very difficult time after the collapse of its communist system.
